C4 Plants Definition
C4 fixation is an addition to the ancestral and more common C3 carbon fixation. Around 95 of plants on earth are C3 plants.

C3 C4 And Cam Plants Bioninja Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
Carbon dioxide comes into the plant via stomata.

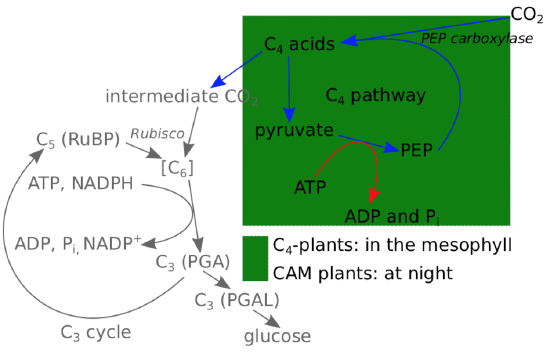
C4 plants definition. Maize there is a special KRANZ ANATOMY in which mesophyll cells are adjacent to bundle sheath cells containing large chloroplasts. C4 plants are plants which cycle carbon dioxide to 4-carbon sugar compounds in order to enter the C3 or the Calvin cycle. C4 plants use this 4-carbon compound to effectively concentrate CO2 around rubisco so that rubisco is.
Some of the plants that we usually consume are C4 plants such as pineapple corn sugar cane etc. The first stable product formed in C4 cycle is a four carbon 4C compound hence the name. Leaves of the C4 plants exhibit Kranz anatomy.
Surrounding the leaves are mesophyll cells that contain a much more active enzyme called phosphoenolpyruvate PEP carboxylase. C4 carbon fixation or the HatchSlack pathway is one of three known photosynthetic processes of carbon fixation in plants. This step takes place in the mesophyll cells that are located close to the stomata where carbon dioxide and oxygen enter the plant.
Today plants that use C4 photosynthesis so-called C4 plants typically grow faster than other plants especially in warmer climates. In the C4 pathway initial carbon fixation takes place in mesophyll cells and the Calvin cycle takes place in bundle-sheath cells. CAM Plants Definition CAM short for Crassulacean Acid Metabolism is a method of carbon fixation evolved by some plants in dry circumstances.
Most C 4 plants have a special leaf anatomy called Kranz anatomy in which the. The C4 plants are very productive in climatic conditions that are hot and dry and produce a lot of energy. These plants are called C4 plants because the first product of carbon fixation is a 4-carbon compound instead of a 3-carbon compound as in C3 or normal plants.
The CO 2 then enters the mesophyll cells. C4 photosynthesis is a biochemical modification of the C3 photosynthesis process in which the C3 style cycle only occurs in the interior cells within the leaf. In C 4 plants eg.
The examples of C4 plants are as follows. A C 4 plant is better adapted than a C 3 plant in an environment with high daytime temperatures intense sunlight drought or nitrogen or CO 2 limitation. These are cells that open and close on a leaf for water and gas exchange.
C4 plantsincluding maize sugarcane and sorghumavoid photorespiration by using another enzyme called PEP during the first step of carbon fixation. Oxaloacetic acid which is unstable and is either reduced to malic acid or aminated to aspartic acid. C3 and C4 plants are two types of plants using C3 and C4 cycles during the dark reaction of photosynthesis respectively.
C4 plants are those plants where the first product of photosynthesis is a 4 carbon compound ie. Very few plants 5 on earth are C4 type. It owes the names to the discovery by Marshall Davidson Hatch and Charles Roger Slack that some plants when supplied with 14CO 2 incorporate the 14C label into four-carbon molecules first.
Carbon fixation in C 4 plants Certain plantsincluding the important crops sugarcane and corn maize as well as other diverse species that are thought to have expanded their geographic ranges into tropical areashave developed a special mechanism of carbon fixation that largely prevents photorespiration. Carbon dioxide combines with 3-carbon phosphenol pyruvate PEP in the mesophyll cells to form 4-carbon oxaloacetic acid and malic acid which are then transported to the bundle sheath cells where carbon dioxide is released to go into the. PEP carboxylase attaches an incoming carbon dioxide molecul to the three-carbon molecule PEP producing oxaloacetate a four-carbon molecule.
C4 plants are so called because the first product of CO2 fixation is a C4 organic acid oxaloacetate formed by the carboxylation of phosphoenolpyruvate PEP by PEP carboxylase. In most plants the stomata which are like tiny mouths that take in oxygen all along the surfaces of their leaves open during the day to take in CO 2 and release O 2. Sugar cane sorghum maize and grasses are C4 plants.
These plants in addition to C3 cycle uses an additional dark reaction pathway called C4 cycle. These are cells that are located toward the surface of a plant leaf and are where photosynthesis. The oxaloacetate is converted to other C4 acids malate or aspartate and transferred to the bundle sheath.
This gives C4 plants such as corn an advantage over their competitors and also helps them to colonize harsh environments that other plants struggle to thrive in. The photosynthetic efficiency of C4 plants is very high due to the absence of photorespiration.

Photosynthesis C3 C4 Cam Plants Ppt Video Online Download Source: slideplayer.com

Plant Photorespiration Biology For Non Majors Ii Source: courses.lumenlearning.com

The Difference Between C3 And C4 Plants Ripe Source: ripe.illinois.edu

C4 Engineering Plants Diagram Quizlet Source: quizlet.com

C3 C4 And Cam Plants Comparison Chart Biology Dictionary Source: biologydictionary.net